4. Trigonometry and the Unit Circle
4.2 The Unit Circle
Class Notes
The McGraw-Hill Ryerson PreCalculus 12 Text is used as the Main Resource.
Assignments in the Powerpoint Lesson Plans refer to pages and questions in the PreCalculus 12 text.
Digital Resources to Enhance Learning and Differentiate Instruction
McGraw Hill Teachers Resource DVD
4.2_193_IA Exploring values on the Unit Circle
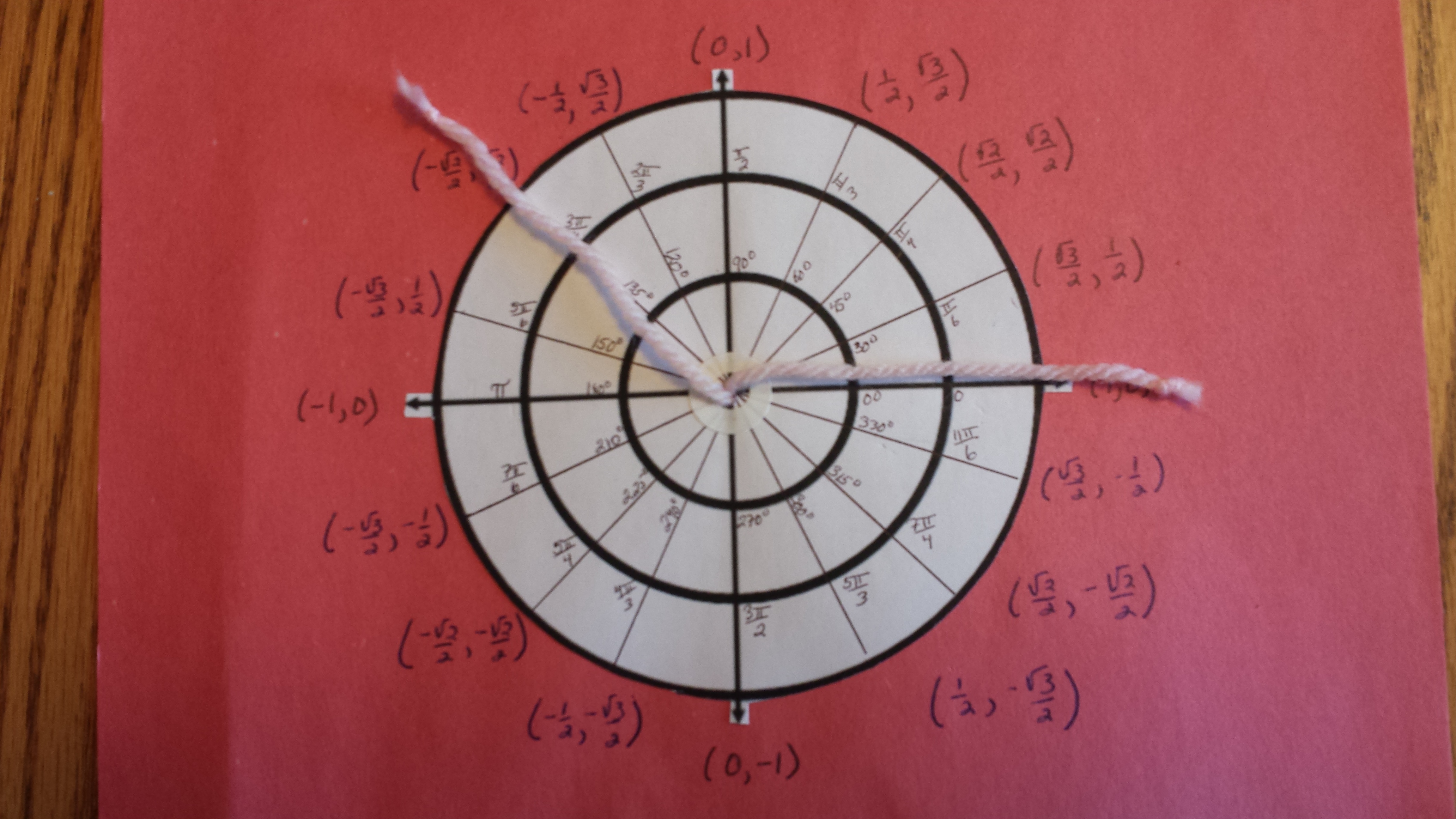
Making a Unit Circle
I wanted students to have a unit circle with movable arms to visualize and simulate angles of rotation and angles in standard position. The first step was to have students cut out and glue the three concentric circles to a sheet of construction paper. They punched a hole through the origin, pushed the two pieces of string (I used yarn for a thicker arm) through the hole and secured the string with a knot. When I was teaching angles in standard position in degrees, students labeled the inner circle with special angle measurments. In our discussion of angles in standard position and rotation angles, students moved the strings to simulate the position of the initial arm and rotation of the terminal arm. This worked will for both positive and negative rotation. The picture below is an example of how we used the unit circle to discuss co-terminal angles.
During the lesson to introduce radians, students labelled the middle circle with angles measured in radians. We cut a piece of string for the length of each radius and curved this length of string along each corresponding curcumference as an introduction to the definition of radian measure as a ratio. Students were surprised to see that each corresponding radius length always ended up in the same location of the terminal arm, one radian.
At last we were ready to discuss the coordinates for the points of intersection of the terminal arm and the unit circle. We labelled the coordinates on the outer circle. Having two movable arms was an advantage for students when we discussed measures of the shortest angle between two points such as (0, 1) and (1/2, -√3/2).
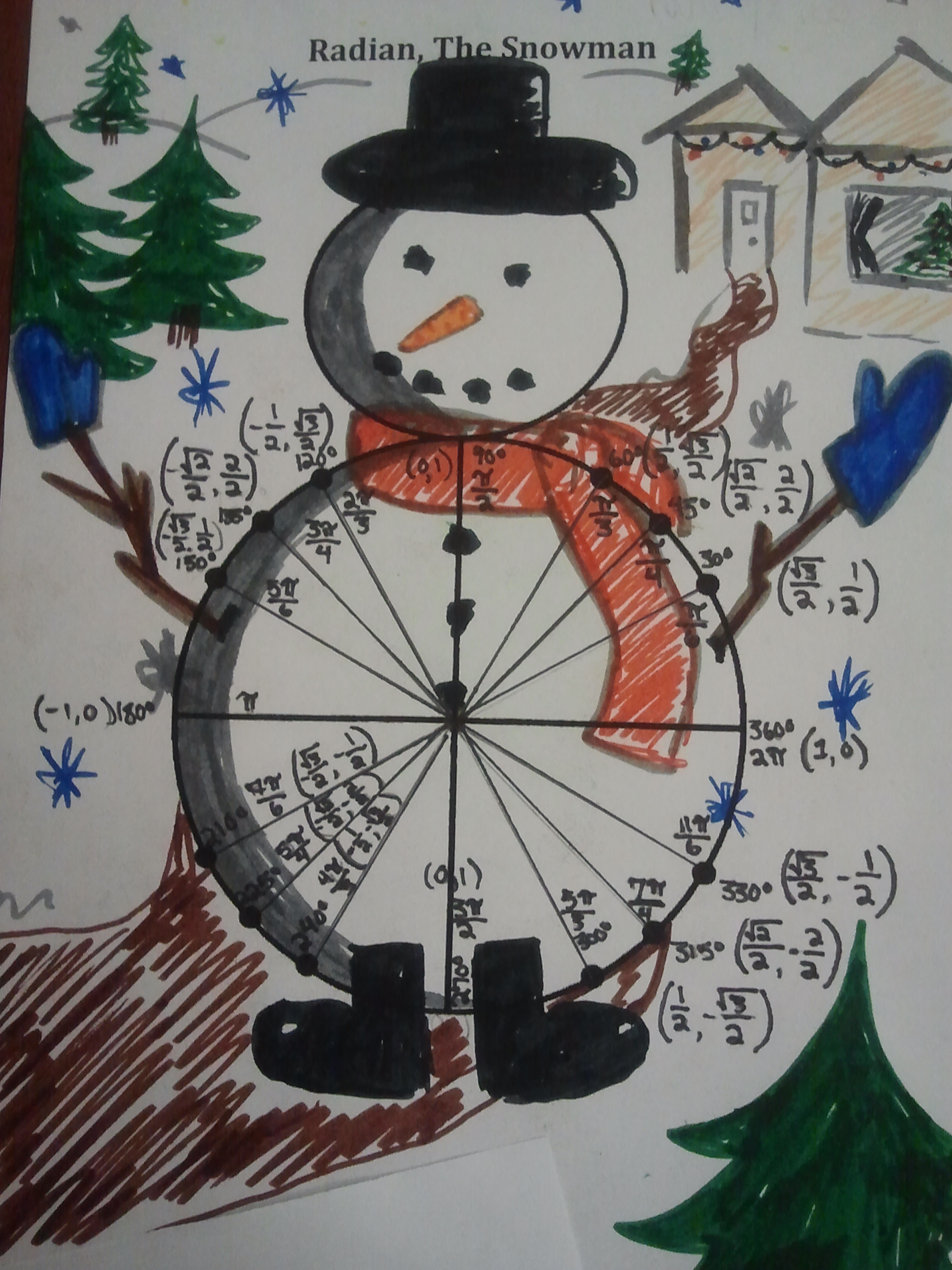
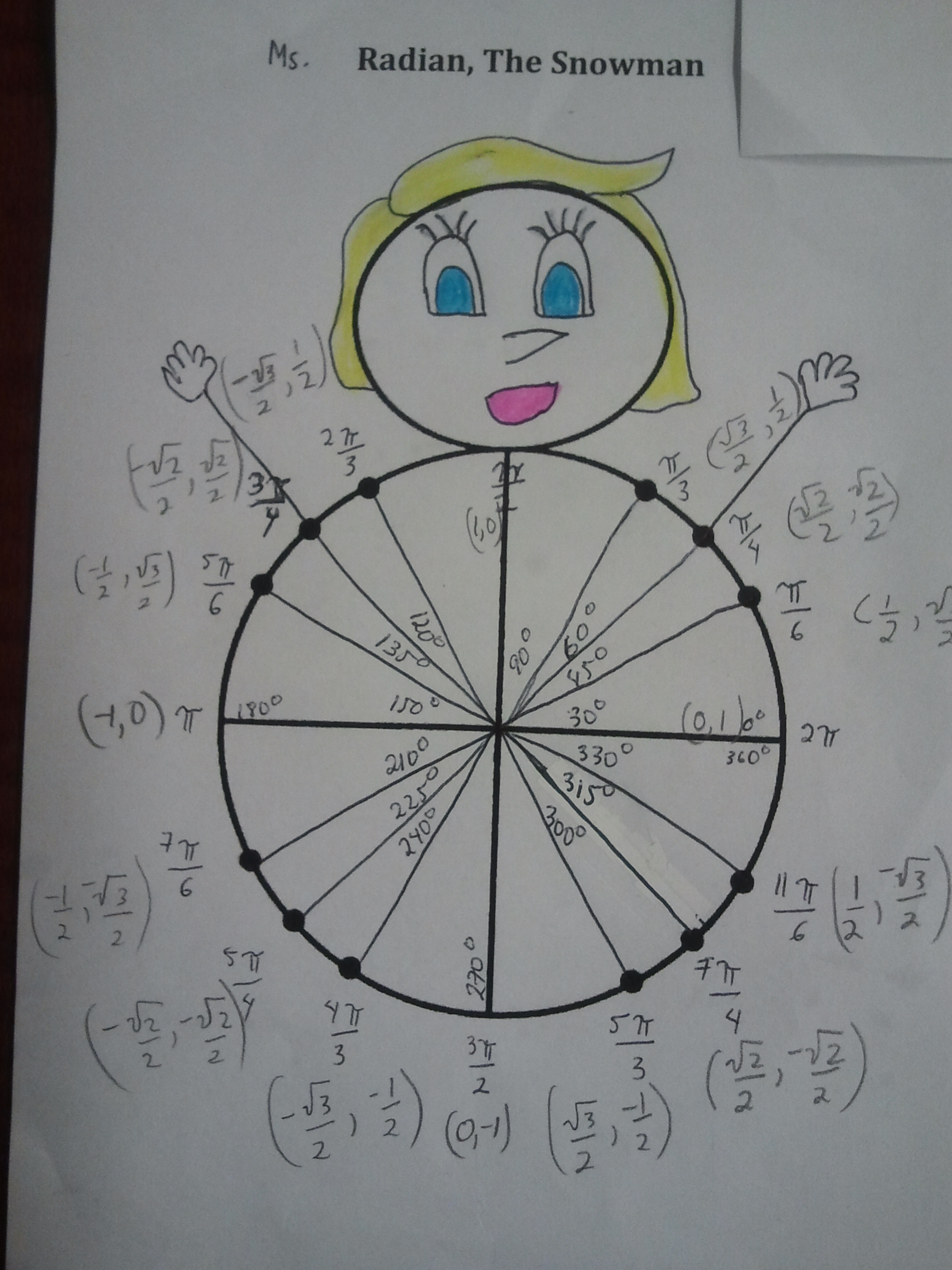
Radian Snowan Activity Download
This is a an activity to help students remember angles in radian measure.