3. Polynomial Functions
Resources for 3. Polynomial Functions
| Site: | ARPDC |
| Course: | ERLCMath 30-1, 2012-2014 - Stephanie MacKay (Click to Enter) |
| Book: | 3. Polynomial Functions |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Saturday, 18 October 2025, 6:21 PM |
Table of contents
- 3. Polynomial Functions
- Polynomial Notes
- The Seven Mathematical Processes Sample Activities for Polynomials
- 3.1 Characteristics of Polynomial Functions
- formative assessment
- 3.2 Remainder Theorem
- remainder theorem formative assessment
- 3.3 The Factor Theorem
- factoring and solving formative assessment
- 3.4 Equations and Graphs of Polynomial Functions
- 3. Polynomial Functions Review
The Seven Mathematical Processes Sample Activities for Polynomials
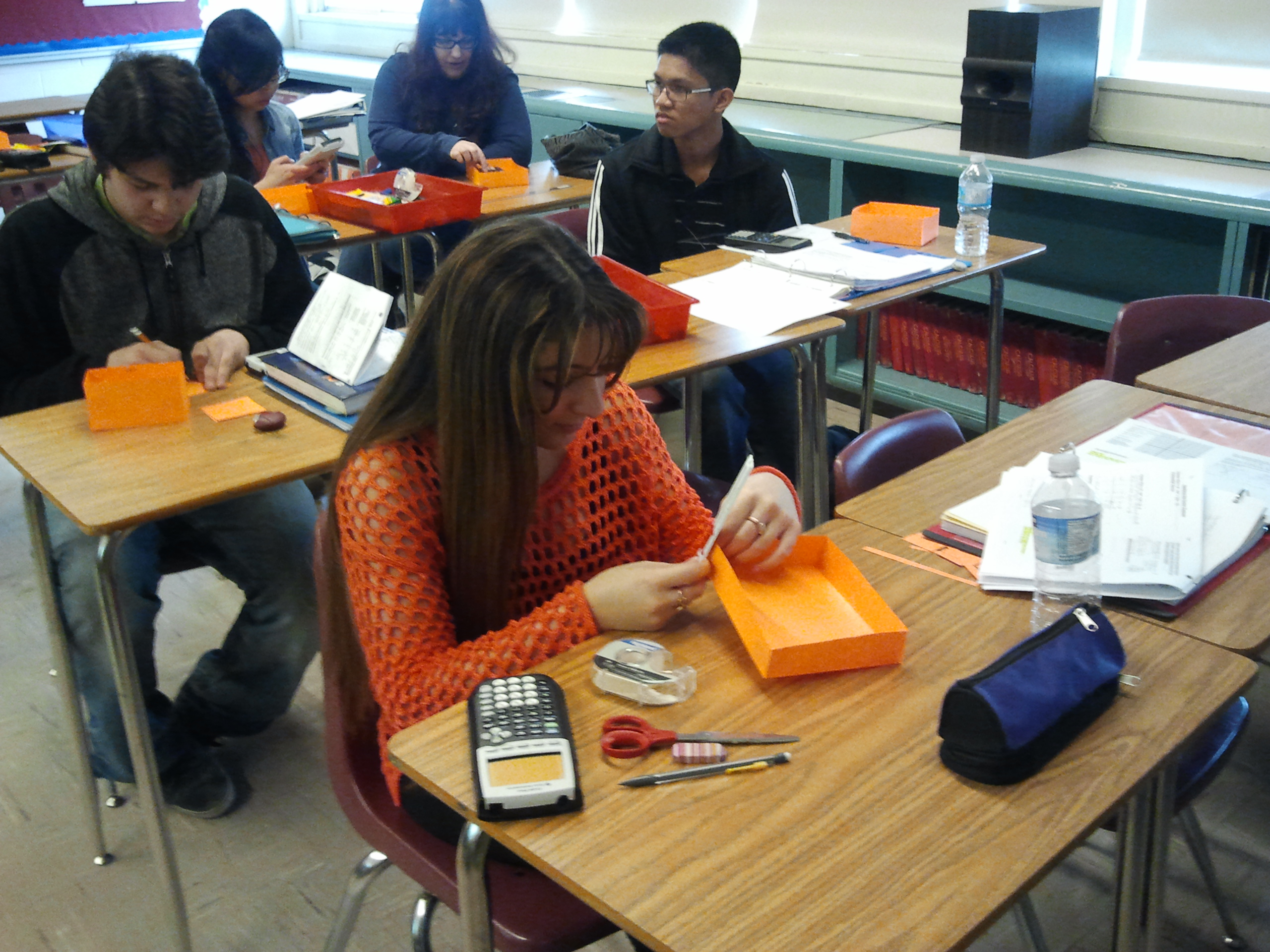
Seven Mathematical Processes: Maximum Volume of a Box Activity .
This activity promoted the following processes: Communication, Connections, Estimation, Problem Solving, Reasoning, Technology, and Visualization. Click here to link to the activity.


Pedagogical Shifts: TRANSFORM, Moving from Traditional to Student-centered.
Shifting from Memorization to Higherlevel Thinking
Shifting from Summative to Formative Assessment
Formative Assessment for Polynomial Functions Group Activity

3.1 Characteristics of Polynomial Functions
Class Notes
The McGraw-Hill Ryerson PreCalculus 12 Text is used as the Main Resource.
Assignments in the Powerpoint Lesson Plans refer to pages and questions in the PreCalculus 12 text.
3.2 Remainder Theorem
Class Notes
The McGraw-Hill Ryerson PreCalculus 12 Text is used as the Main Resource.
Assignments in the Powerpoint Lesson Plans refer to pages and questions in the PreCalculus 12 text.
3.3 The Factor Theorem
Class Notes
The McGraw-Hill Ryerson PreCalculus 12 Text is used as the Main Resource.
Assignments in the Powerpoint Lesson Plans refer to pages and questions in the PreCalculus 12 text.
Digital Resources
![]() 3.3B The Classic Box Problem Exploration
3.3B The Classic Box Problem Exploration
Pedagogical Shifts: TRANSFORM, Moving from Traditional to Students Centered.
Shifting from Student as Knowledge Recipient to Student as Inquirer and Creator
Moving from Short-term Assignments to Project-based Learning
Moving from Memorization to Higher-level Thinking
Moving from One-size-fits-all to Personalized, Differentiated
Moving from Print-based to Multimodal (print, visual, digital)
The following activity promotes learning mathematics using the Mathematical Processess.
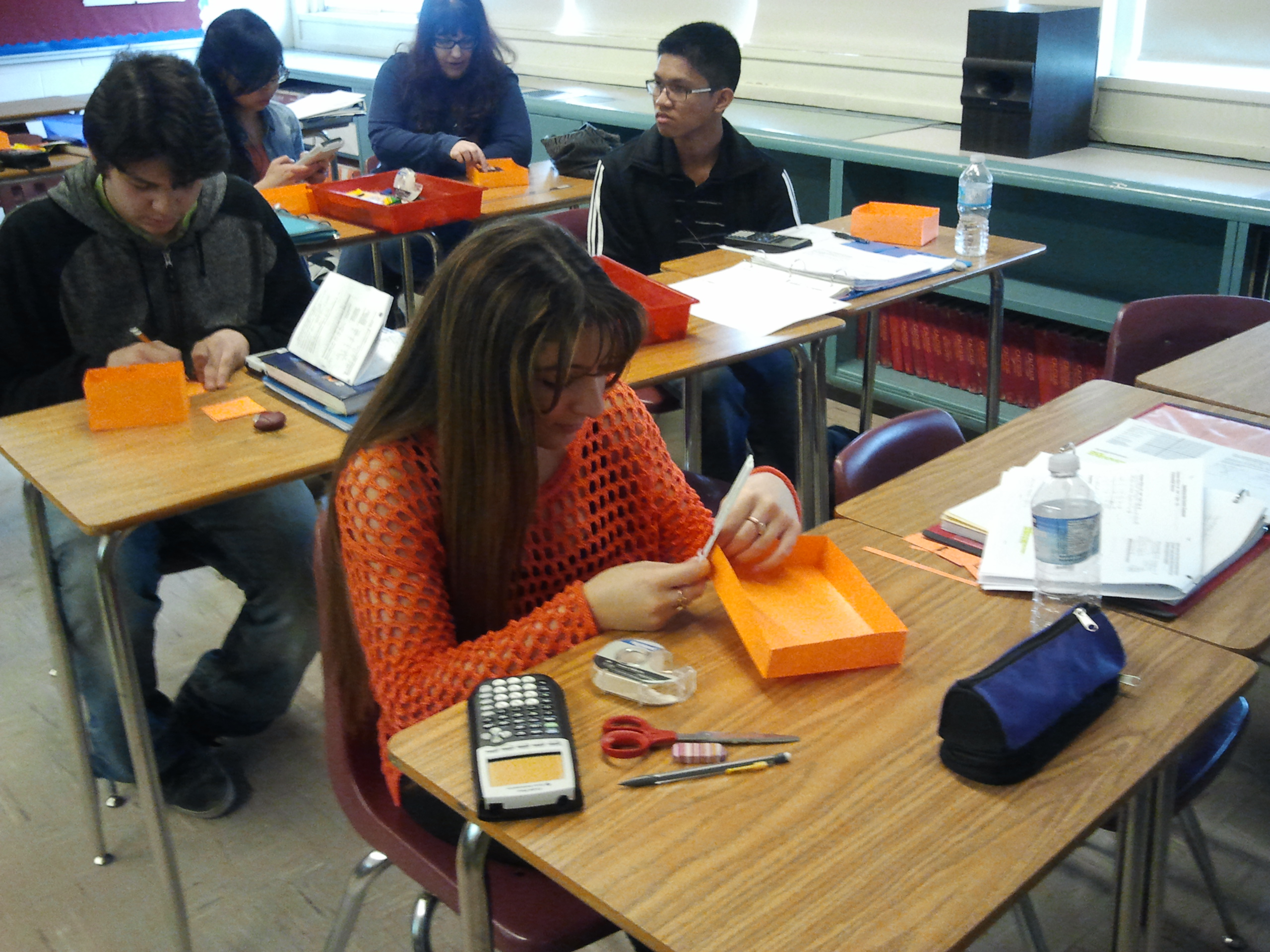


Click this link to learn more about Problem Solving: Maximum Volume of a Box with No Lid Activity
3.4 Equations and Graphs of Polynomial Functions
Class Notes
The McGraw-Hill Ryerson PreCalculus 12 Text is used as the Main Resource.
Assignments in the Powerpoint Lesson Plans refer to pages and questions in the PreCalculus 12 text.
![]() 3.4 Equations and Graphs of Polynomial Functions
3.4 Equations and Graphs of Polynomial Functions
![]() 3.4 Equations and Graphs of Polynomial Functions Revised
3.4 Equations and Graphs of Polynomial Functions Revised
![]() 3.4 Equations and Graphs of Polynomial Functions
3.4 Equations and Graphs of Polynomial Functions
Copyright: McGraw Hill. Located on Teacher Resource Digital DVD.
Digital Resources
![]() Multiplicity of Zeros of Functions
Multiplicity of Zeros of Functions
Pedagogical Shifts: TRANSFORM, Moving from Traditional to Student-centered.
Shifting from Student as Knowledge Recipient to Student as Inquirer and Creator
Shifting from Summative to Formative Assessmnet
Shifting from Competitive to Collaborative Learning
Match My Graph Activity: Formative Assessment

Watch the video to learn more about this Formative Assessment Activity